Introduction
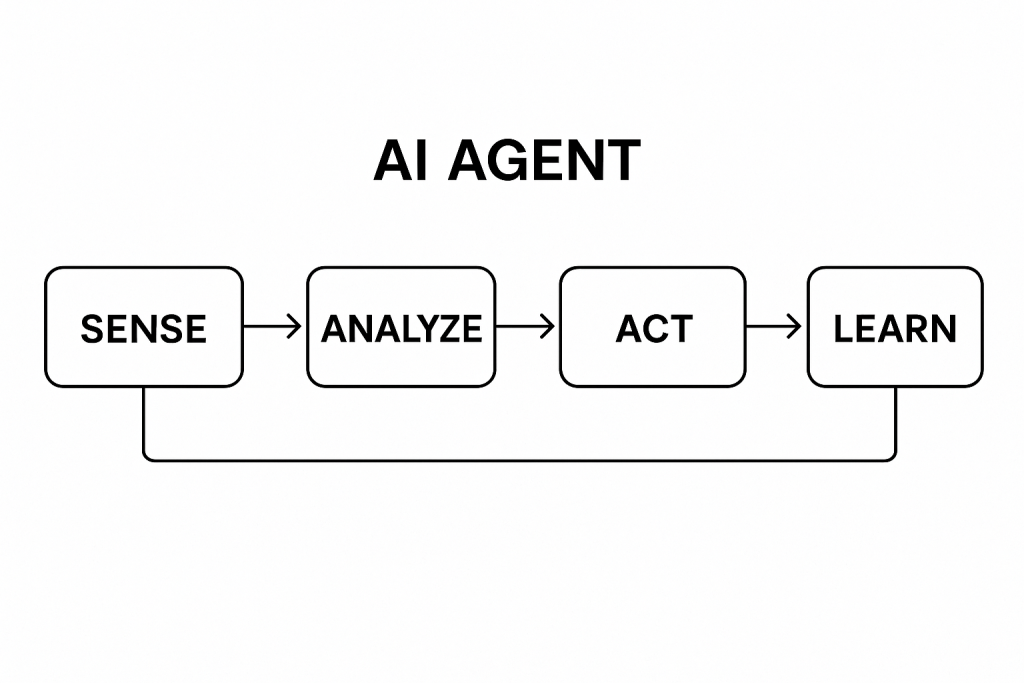
Have you ever wondered how artificial intelligence (AI) systems make decisions or take actions like a human would? The answer lies in AI agents. It is a specialized software that perceives its environment, makes decisions, and acts to achieve specific goals.
With industries rapidly adopting AI, the AI agents market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 46.3%, reaching $52.62 billion by 2030. This explosive growth is fueled by rising automation, smarter decision-making, and the demand for personalized digital experiences.
That’s why understanding the different types of AI agents, their benefits, and real-world examples is key to leveraging these technologies in your personal life or business. Let’s explore.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are autonomous systems designed to sense their surroundings, reason, and act in ways that help accomplish particular objectives. To dive deeper into the AI agents’ definition and types, you can explore this detailed guide.
Unlike simple programs, AI agents can adapt, learn, and interact with dynamic environments. This allows them to handle complex workflows, from customer support chatbots to autonomous vehicles.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents vary widely depending on their sophistication and purpose. Here are the main types you should know about:
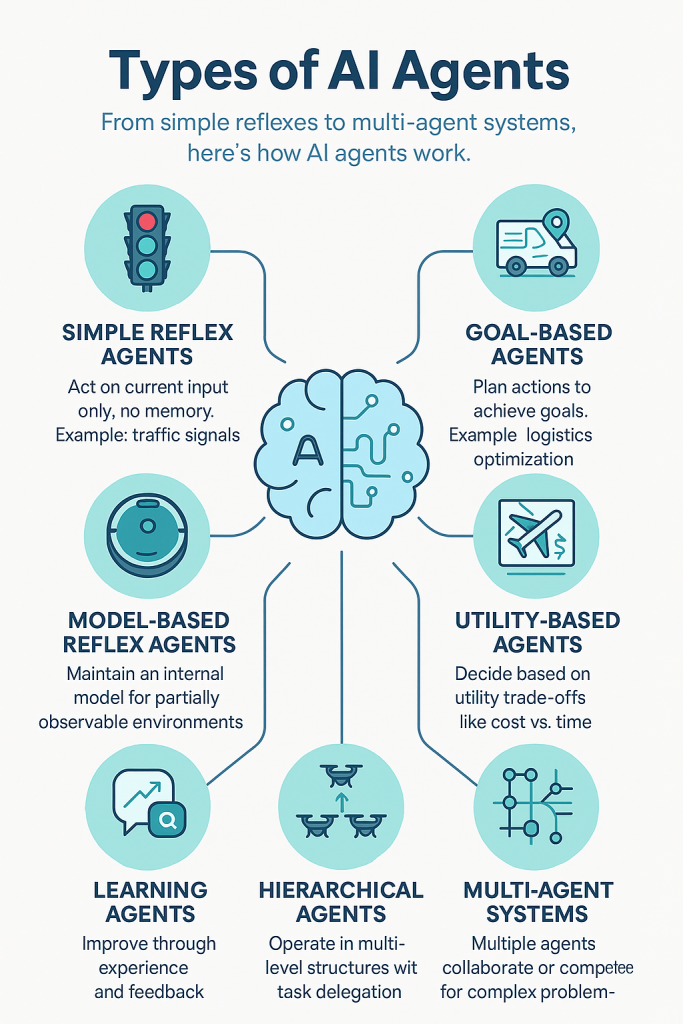
- Simple Reflex Agents
These act purely on current inputs with predefined rules, without memory or learning capabilities. For example, a traffic signal that changes lights at fixed intervals is a simple reflex agent.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents
These improve upon simple reflex agents by maintaining an internal model of the world to manage partially observable environments. Robot vacuum cleaners that map your room to clean efficiently use this type.
- Goal-Based Agents
These agents move beyond immediate reactions by planning and selecting actions to achieve specific goals. They evaluate future consequences of possible actions, such as a logistics routing system optimizing delivery paths.
- Utility-Based Agents
These agents decide based on a utility function that quantifies the desirability of outcomes. They aim to maximize benefit, balancing trade-offs like cost versus time. An example is a flight booking assistant recommending routes with the best balance of price and travel time.
- Learning Agents
Learning agents improve their performance by learning from experience and adapting to changes in the environment over time. AI chatbots that become smarter with use are good examples.
- Hierarchical Agents
These agents operate in a multi-level structure where higher-level agents delegate tasks to lower-level ones. Drone delivery systems often use hierarchical agents to manage complex coordination.
- Multi-Agent Systems
These involve multiple interacting agents that may collaborate or compete to solve problems too complex for a single agent. Smart traffic control systems with multiple sensors and controllers are classic examples.
Benefits of AI Agents
When you use AI agents, you unlock several advantages that can transform how you work and live:
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks
AI agents take over repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing you to focus on more strategic and creative work. This boosts efficiency by reducing manual effort and speeding up workflows.
- Improved Decision-Making
By analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time, AI agents provide you with actionable insights and predictions. This empowers you to make faster, smarter decisions that can lead to improved business outcomes.
- Personalized Experiences
AI agents learn from interactions to offer personalized responses and tailored recommendations. This enhances customer satisfaction by effectively meeting individual preferences.
- 24/7 Availability
Unlike human workers, AI agents work nonstop without fatigue, providing continuous support and service. This ensures your operations and customer services are uninterrupted.
- Scalability and Flexibility
AI agents can easily scale to handle increased workloads and adapt to changing business needs. This flexibility supports growth and fluctuating demands efficiently.
- Cost Reduction
By automating complex and routine processes, AI agents reduce operational costs and minimize human error. This leads to better resource utilization and higher return on investment.
Real-World Examples of AI Agents
AI agents are already revolutionizing multiple industries. Let’s explore how:
- Healthcare
In healthcare, AI agents assist in diagnostics, personalized treatment planning, and patient monitoring. For instance, AI diagnostic tools analyze medical images to detect diseases earlier than traditional methods, improving patient outcomes.
- Finance
AI agents automate fraud detection, risk assessment, and personalized financial advice. They analyze transaction patterns in real-time, preventing fraud and guiding investment decisions.
- Retail & E-commerce
AI agents power personalized shopping experiences, chatbots for customer queries, and inventory management. Amazon’s recommendation engine is a prime example, improving sales by suggesting products tailored to your preferences.
- Smart Homes
From voice assistants that control lighting and appliances to smart thermostats optimizing energy use, AI agents make homes more comfortable and efficient.
- Transportation
Autonomous vehicles rely on AI agents to navigate, avoid obstacles, and optimize routes, promising safer and more efficient travel.
- Business
AI agents automate workflows like email filtering, meeting scheduling, and customer relationship management, boosting productivity and reducing manual errors.
- Additional Applications
Beyond these sectors, AI agents find use in education, where they offer personalized learning; agriculture, optimizing crop yields through sensor data; and cybersecurity, proactively detecting threats and responding in real-time.
To Sum Up
Now that you know the different types of AI agents and their powerful benefits, you’re better equipped to harness AI’s potential in your daily life or business. These intelligent systems offer scalable, adaptive solutions that improve efficiency and decision-making across industries, paving the way for a smarter future.
Harness the intelligence of AI agents to transform how you work, live, and innovate!
If you want to go beyond the basics and gain practical skills in AI, check out Gignaati AI Agents Masterclass for hands-on learning and expert insights.
Frequently Asked Question
What does an AI agent do?
An AI agent autonomously perceives its environment, makes decisions, and takes actions to achieve specific goals. It acts like a digital assistant that performs tasks on your behalf without constant human input.
How do AI agents work?
AI agents gather data from their surroundings, analyze it using algorithms, and decide the best course of action. They then execute these actions and learn from feedback to improve over time.
Which is the most powerful AI agent?
The most powerful AI agents are those combining advanced reasoning, learning, and planning capabilities, often called learning or goal-based agents. Examples include AI models like OpenAI’s GPT-based assistants that adapt and perform complex tasks.
How to pick the right AI agent?
Select an AI agent based on your specific goals, environment complexity, and the tasks you want automated. Evaluate whether you need simple rule-based agents or advanced learning agents for dynamic decision-making.
Is Siri an AI agent?
Yes, Siri is an AI agent that uses natural language processing to understand and respond to voice commands. It automates tasks like setting reminders, answering questions, or controlling smart devices.
What are examples of AI agents?
Common AI agents include virtual assistants like Alexa, autonomous vehicles, recommendation engines, customer support chatbots, and robotic process automation bots used in businesses.